- Introduction to the Internet
The Internet is a global network of interconnected computers that communicate using standard protocols. Every device connected to the internet needs a unique address to identify itself.
- What Is a Domain Name?
A Domain Name is a human-readable address used to access a website on the internet. Example : www.codekilla.com
- Why Domain Names Are Needed
- Easy to remember
- Represents brand identity
- Replaces numeric IP addresses
- Essential for businesses and professionals
- Structure of a Domain Name
|
Part |
Example |
Full Form |
|---|---|---|
|
Subdomain |
www |
World Wide Web (commonly used, but technically optional) |
|
SLD |
codekilla |
Second-Level Domain |
|
TLD |
.com |
Top-Level Domain |
|
“www” stands for World Wide Web, but it's not required for a website to function. Many modern sites work without it ( |
||
- Types of Domain Extensions
gTLD – Generic Top-Level Domain
- .com – Commercial
- .org – Organization
- .net – Network
- .tech – Technology
- .ai – Artificial Intelligence
ccTLD – Country Code Top-Level Domain
- .in – India
- .us – United States
- uk – United Kingdom
nTLD – New Top-Level Domain
- .dev – Developer
- .io – Input / Output
- .design – Creative field
- What Is DNS?
DNS – Domain Name System
DNS converts domain names into IP addresses so browsers can locate web servers.
codekilla.com → 192.168.1.1
DNS works like the Internet’s phonebook.
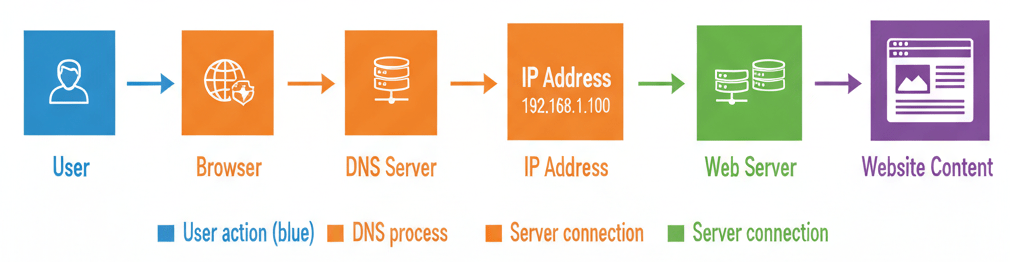
- How DNS Works (Step-by-Step)
- User types a domain name. Example: www.codekilla.com
- Browser queries DNS server. The browser asks the DNS resolver: “What is the IP address for this domain?”
- DNS returns IP address. Example: 192.0.2.1
- Browser connects to server. Using the IP address, the browser establishes a connection with the web server.
- Website loads. The server responds with the website content, and the page is displayed.
- What Is an IP Address?
IP Address – Internet Protocol Address
An IP address uniquely identifies a device on a network.
Methods to Find a Domain’s IP Address
- Open Command Prompt - Press Windows Key + R - Type cmd and press Enter
- Type nslookup codekilla.com
- DNS server queried
- IP address returned
- Result displayed in Command Prompt
Note: If the domain uses a CDN (like Cloudflare), the IP shown may belong to the CDN rather than the origin server.
- Types of IP Addresses
IPv4 : Internet Protocol Version 4
- IPv4 addresses are made up of 32 bits, divided into 4 octets (8 bits each).
- Each octet is written in decimal format, ranging from 0 to 255.
- The format is called dotted-decimal notation: Example → 192.168.1.1
|
Octet |
Binary (8 bits) |
Decimal |
|---|---|---|
|
1st |
11000000 |
192 |
|
2nd |
10101000 |
168 |
|
3rd |
00000001 |
1 |
|
4th |
00000001 |
1 |
- Each octet is converted from binary to decimal.
- Together, they form the full IP address: 192.168.1.1
Optional: Convert to Single Decimal Number
You can also convert the full IP into a single 32-bit decimal number using this formula:
So 192.168.1.1 = 3232235777 in pure decimal format
- Dotted-decimal is human-friendly.
- Pure decimal is used in some network tools, databases, and low-level configurations.
- Total Addresses : 2 32 = 4.3 billion
IPv6 : Internet Protocol Version 6
- IPv6 is the 128-bit successor to IPv4 (which is 32-bit).
- It allows for vastly more unique addresses — about 3.4 × 10 38 possible combinations.
- IPv6 addresses are written in hexadecimal format, not decimal like IPv4.
- It consists of 8 groups of 4 hexadecimal digits.
- Each group represents 16 bits.
- Total: 8 × 16 = 128 bits.
- Example : 2001:0db8:85a3:0000:0000:8a2e:0370:7334
|
Segment |
Hex Value |
Binary (16 bits) |
|---|---|---|
|
1 |
2001 |
0010000000000001 |
|
2 |
0db8 |
0000110110111000 |
|
3 |
85a3 |
1000010110100011 |
|
4 |
0000 |
0000000000000000 |
|
5 |
0000 |
0000000000000000 |
|
6 |
8a2e |
1000101000101110 |
|
7 |
0370 |
0000001101110000 |
|
8 |
7334 |
0111001100110100 |
- Omit leading zeros: 0370 → 370
- Use double colons (::) to compress consecutive zeros: 2001:0db8:0000:0000:0000:0000:1428:57ab → 2001:db8::1428:57ab
- Total Addresses : 2 128 ≈ 340 undecillion
- DNS Records
|
Record |
Full Form |
Purpose |
Example |
|---|---|---|---|
|
A |
Address Record |
Maps to IPv4 |
example.com → 192.168.1.1 |
|
AAAA |
Quad-A Record |
Maps to IPv6 |
example.com → 2001:db8::1 |
|
CNAME |
Canonical Name |
Domain alias |
www.example.com → example.com |
|
MX |
Mail Exchange |
Email routing |
mail.google.com |
|
TXT |
Text Record |
Verification |
SPF / DKIM |
|
NS |
Name Server |
DNS authority |
ns1.host.com |







